NANJING ALAS INTERNATIONAL CO., LTD
L/C, T/T, Paypal, Money Gram
| Availability: | |
|---|---|
| Quantity: | |
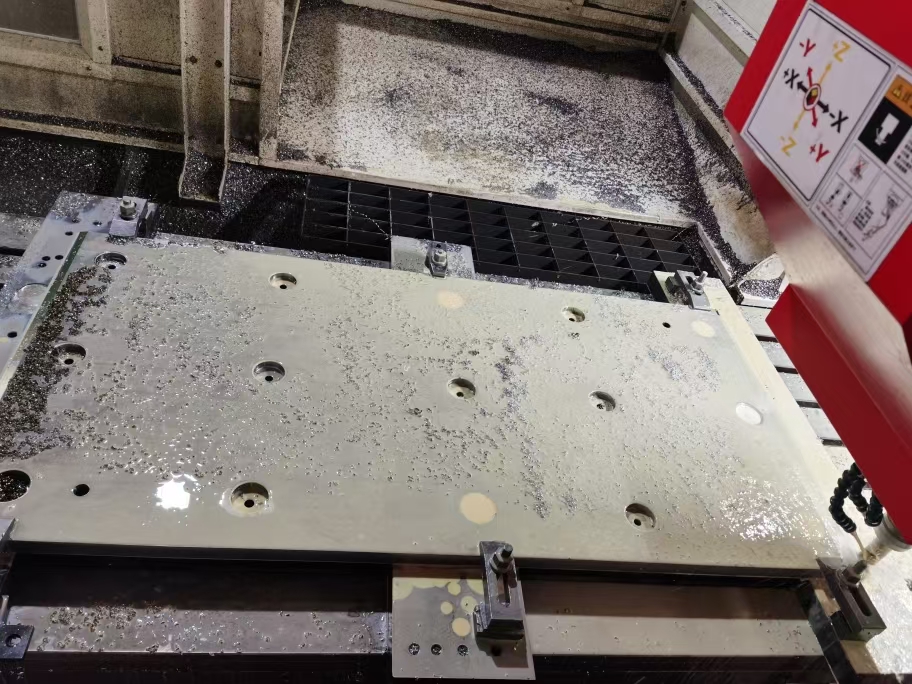
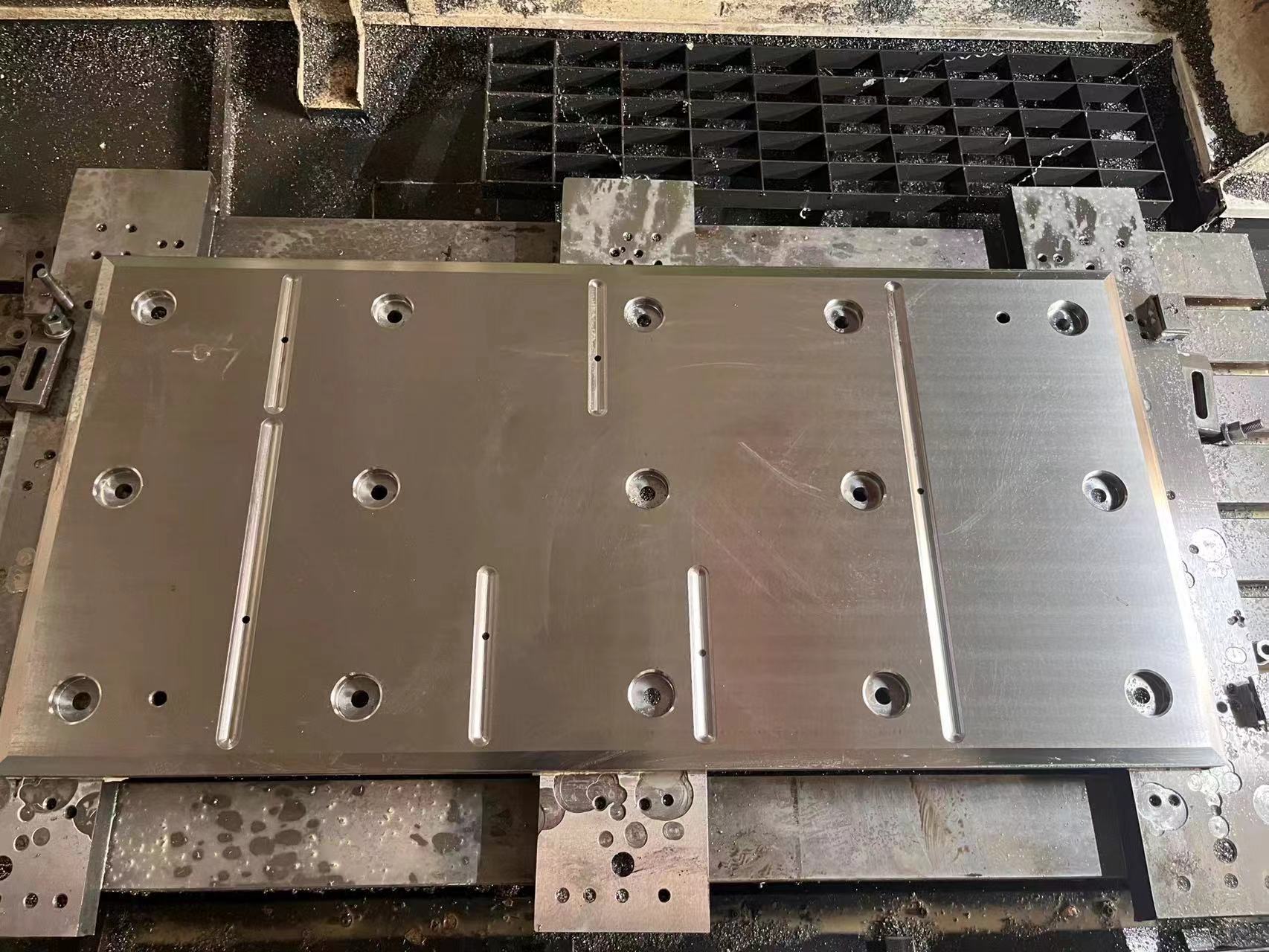
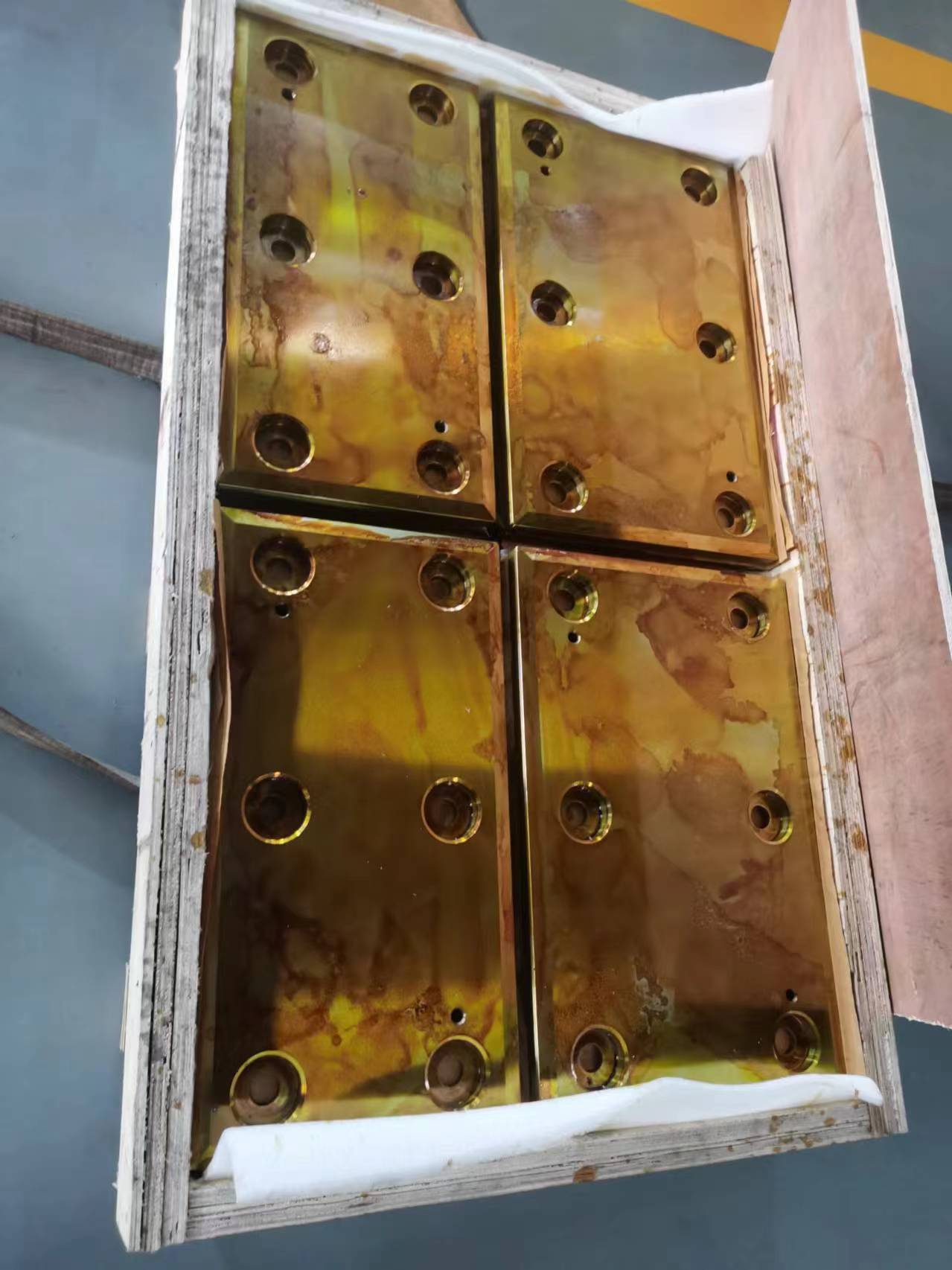
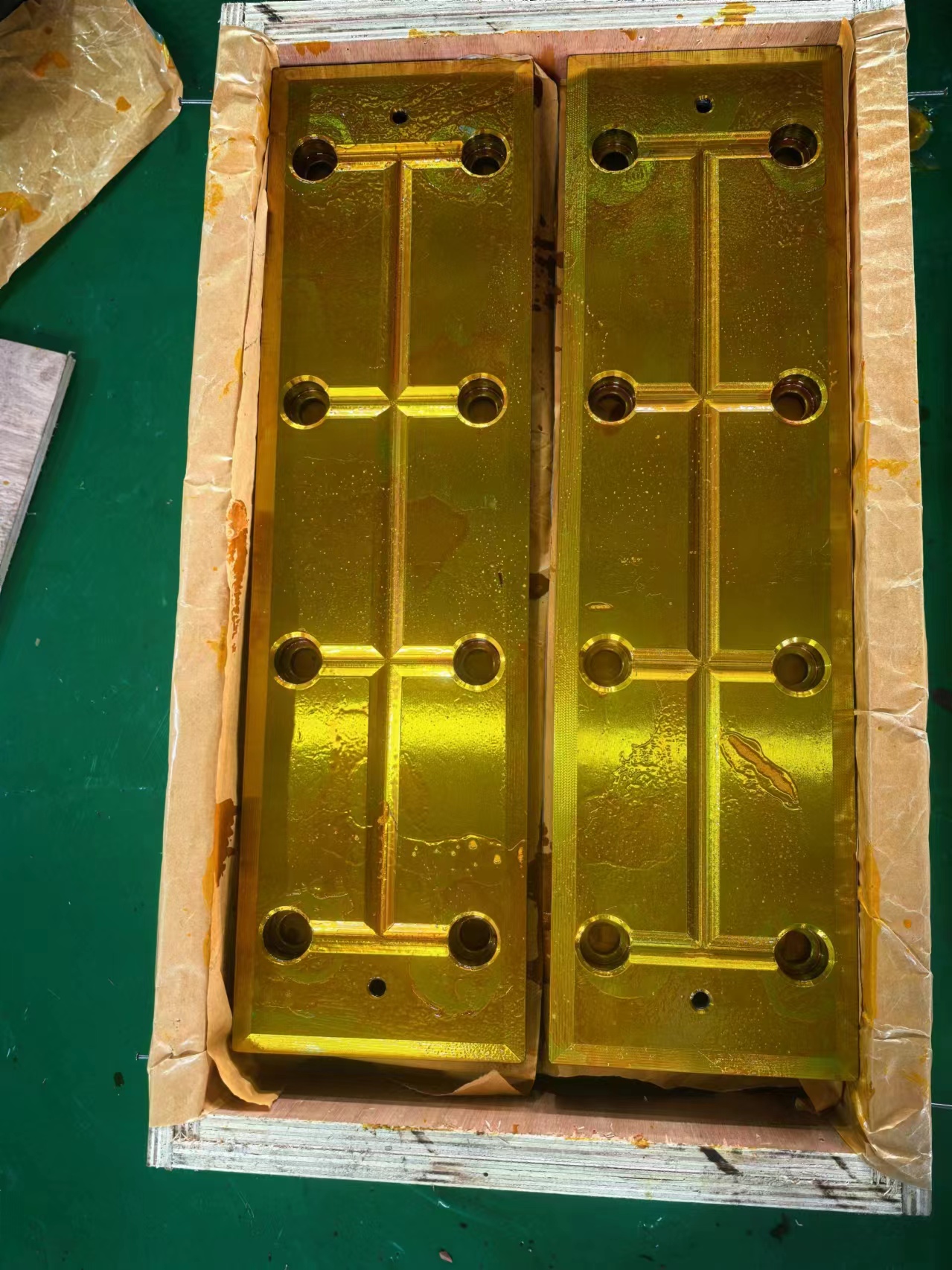
Rolling mill wear plates/liners are considered critical "protective structural components" that ensure the long-term and stable operation of rolling mills. They are key interface components installed on the inner walls of the large rolling mill housing windows, supporting and guiding the bearing chocks.
I. Core Functions of Rolling Mill Wear Plates
The wear plates perform multiple tasks in the complex mechanical environment of the rolling mill, and their performance directly affects the production line's operating rate and equipment lifespan:
"Protective Armor" for the Mill Housing:
The rolling mill housing is the most valuable and largest fixed component of the rolling mill. During the rolling process, the bearing chocks frequently move up and down (for reduction adjustment) or back and forth. Without wear plates, the bearing chocks would directly wear down the housing. As a "consumable part," the wear plate protects the expensive housing from direct damage by actively absorbing wear, thus transforming expensive housing repairs into simple wear plate replacements.
Precise Guid
Rolling mill wear plates/liners are considered critical "protective structural components" that ensure the long-term and stable operation of rolling mills. They are key interface components installed on the inner walls of the large rolling mill housing windows, supporting and guiding the bearing chocks.
The wear plates perform multiple tasks in the complex mechanical environment of the rolling mill, and their performance directly affects the production line's operating rate and equipment lifespan:
The rolling mill housing is the most valuable and largest fixed component of the rolling mill. During the rolling process, the bearing chocks frequently move up and down (for reduction adjustment) or back and forth. Without wear plates, the bearing chocks would directly wear down the housing. As a "consumable part," the wear plate protects the expensive housing from direct damage by actively absorbing wear, thus transforming expensive housing repairs into simple wear plate replacements.
To ensure uniform thickness of the rolled steel plates, the roll bearing chocks must maintain vertical and stable movement within the housing window. The wear plates provide a stable guide for the bearing chocks. They not only limit the horizontal swing of the bearing chocks but also ensure that the rolls maintain their predetermined geometric centerline under immense pressure.
At the moment the steel billet is fed into the rolls (impact load), violent vibrations and reaction forces are generated. The wear plates are responsible for evenly transmitting thousands of tons of rolling force to the housing and also act as a buffer, absorbing and dissipating some of the impact energy to prevent stress fatigue cracks in the housing.
The inside of the rolling mill is filled with cooling water, emulsion, and scale. The surface of the wear plate, in conjunction with the lubrication system, forms a physical barrier, preventing extremely hard scale from falling between the friction pairs and causing abrasion. It also acts to isolate cooling water and slow down the electrochemical corrosion of the housing.
Installed on the force-bearing surfaces of the work roll and support roll bearing chocks.
Used on the movement trajectories of the push heads and guide plates before and after the rolling mill to withstand the violent impact of the metal billets.
Ensures that the heavy roll sets can slide smoothly when entering and exiting the mill stand without damaging the stand base.



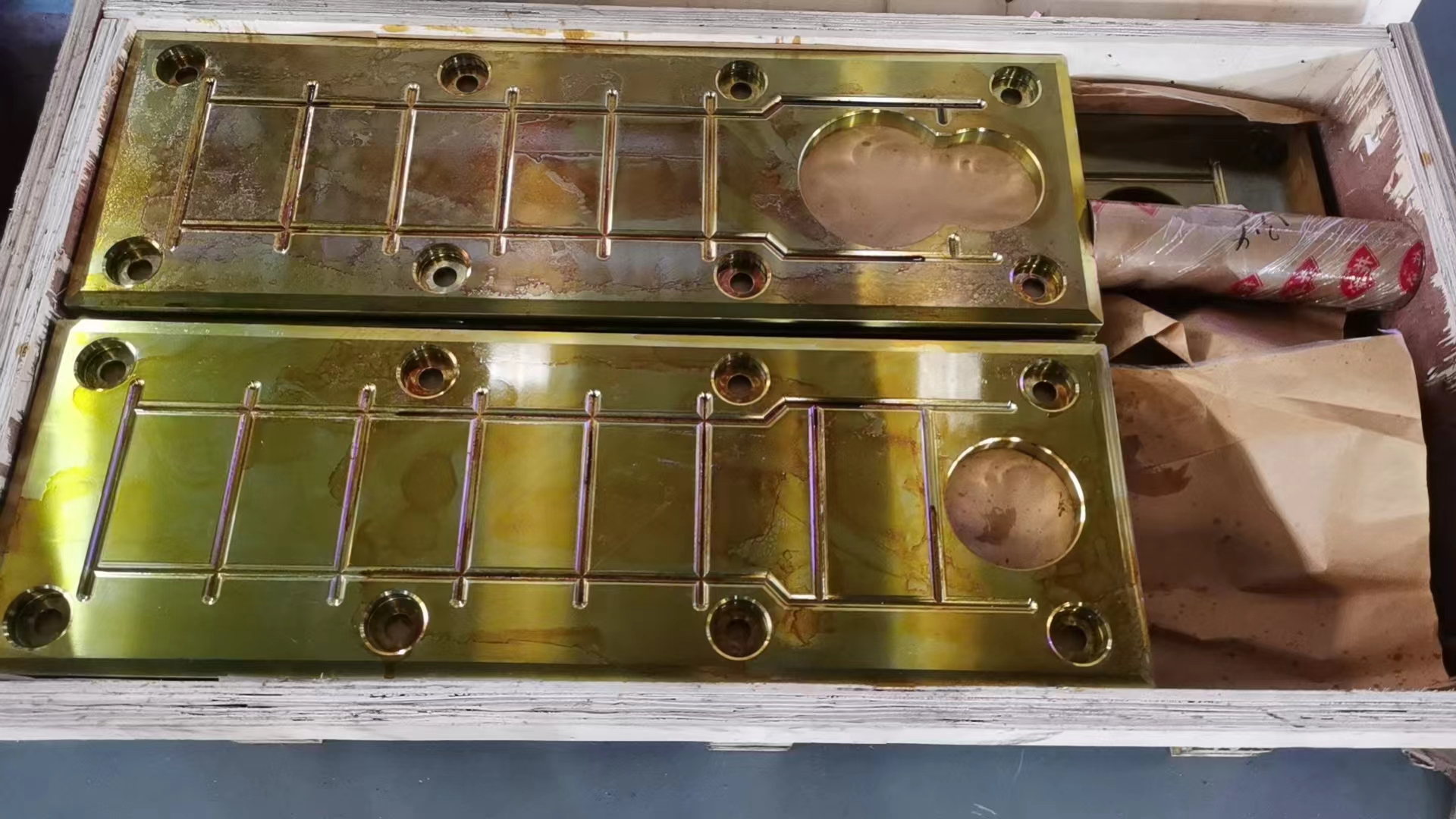


Rolling mill wear plates/liners are considered critical "protective structural components" that ensure the long-term and stable operation of rolling mills. They are key interface components installed on the inner walls of the large rolling mill housing windows, supporting and guiding the bearing chocks.
I. Core Functions of Rolling Mill Wear Plates
The wear plates perform multiple tasks in the complex mechanical environment of the rolling mill, and their performance directly affects the production line's operating rate and equipment lifespan:
"Protective Armor" for the Mill Housing:
The rolling mill housing is the most valuable and largest fixed component of the rolling mill. During the rolling process, the bearing chocks frequently move up and down (for reduction adjustment) or back and forth. Without wear plates, the bearing chocks would directly wear down the housing. As a "consumable part," the wear plate protects the expensive housing from direct damage by actively absorbing wear, thus transforming expensive housing repairs into simple wear plate replacements.
Precise Guid
Rolling mill wear plates/liners are considered critical "protective structural components" that ensure the long-term and stable operation of rolling mills. They are key interface components installed on the inner walls of the large rolling mill housing windows, supporting and guiding the bearing chocks.
The wear plates perform multiple tasks in the complex mechanical environment of the rolling mill, and their performance directly affects the production line's operating rate and equipment lifespan:
The rolling mill housing is the most valuable and largest fixed component of the rolling mill. During the rolling process, the bearing chocks frequently move up and down (for reduction adjustment) or back and forth. Without wear plates, the bearing chocks would directly wear down the housing. As a "consumable part," the wear plate protects the expensive housing from direct damage by actively absorbing wear, thus transforming expensive housing repairs into simple wear plate replacements.
To ensure uniform thickness of the rolled steel plates, the roll bearing chocks must maintain vertical and stable movement within the housing window. The wear plates provide a stable guide for the bearing chocks. They not only limit the horizontal swing of the bearing chocks but also ensure that the rolls maintain their predetermined geometric centerline under immense pressure.
At the moment the steel billet is fed into the rolls (impact load), violent vibrations and reaction forces are generated. The wear plates are responsible for evenly transmitting thousands of tons of rolling force to the housing and also act as a buffer, absorbing and dissipating some of the impact energy to prevent stress fatigue cracks in the housing.
The inside of the rolling mill is filled with cooling water, emulsion, and scale. The surface of the wear plate, in conjunction with the lubrication system, forms a physical barrier, preventing extremely hard scale from falling between the friction pairs and causing abrasion. It also acts to isolate cooling water and slow down the electrochemical corrosion of the housing.
Installed on the force-bearing surfaces of the work roll and support roll bearing chocks.
Used on the movement trajectories of the push heads and guide plates before and after the rolling mill to withstand the violent impact of the metal billets.
Ensures that the heavy roll sets can slide smoothly when entering and exiting the mill stand without damaging the stand base.








